Richest 62 People Own as Much as Half of World's Population
The vast and growing gap between rich and poor has been laid bare in a new Oxfam report showing that the 62 richest billionaires own as much wealth as the poorer half of the world’s population.
Timed to coincide with this week’s gathering of many of the super-rich at the annual World Economic Forum in Davos, the report calls for urgent action to deal with a trend showing that 1% of people own more wealth than the other 99% combined.
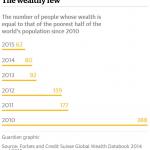
Oxfam said that the wealth of the poorest 50% dropped by 41% between 2010 and 2015, despite an increase in the global population of 400m. In the same period, the wealth of the richest 62 people increased by $500bn (£350bn) to $1.76tn.
The charity said that, in 2010, the 388 richest people owned the same wealth as the poorest 50%. This dropped to 80 in 2014 before falling again in 2015.
Mark Goldring, the Oxfam GB chief executive, said: “It is simply unacceptable that the poorest half of the world population owns no more than a small group of the global super-rich – so few, you could fit them all on a single coach.
“World leaders’ concern about the escalating inequality crisis has so far not translated into concrete action to ensure that those at the bottom get their fair share of economic growth. In a world where one in nine people go to bed hungry every night, we cannot afford to carry on giving the richest an ever bigger slice of the cake.”
Leading figures from Pope Francis to Christine Lagarde, the managing director of the International Monetary Fund, have called for action to reverse the trend in inequality, but Oxfam said words had not been translated into action. Its prediction that the richest 1% would own the same wealth as the poorest 50% by 2016 had come true a year earlier than expected.
The World Economic Forum in Davos comes amid fears that the turmoil in financial markets since the turn of the year may herald the start of a new phase to the global crisis that began eight years ago – this time originating in the less-developed emerging countries.
Oxfam said a three-pronged approach was needed: a crackdown on tax dodging; higher investment in public services; and higher wages for the low paid. It said a priority should be to close down tax havens, increasingly used by rich individuals and companies to avoid paying tax and which had deprived governments of the resources needed to tackle poverty and inequality.
Three years ago, David Cameron told the WEF that the UK would spearhead a global effort to end aggressive tax avoidance in the UK and in poor countries, but Oxfam said promised measures to increase transparency in British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies, such as the Cayman Islands and British Virgin Islands, had not been implemented.
Goldring said: “We need to end the era of tax havens which has allowed rich individuals and multinational companies to avoid their responsibilities to society by hiding ever increasing amounts of money offshore.
“Tackling the veil of secrecy surrounding the UK’s network of tax havens would be a big step towards ending extreme inequality. Three years after he made his promise to make tax dodgers ‘wake up and smell the coffee’, it is time for David Cameron to deliver.”
Oxfam cited estimates that rich individuals have placed a total of $7.6tn in offshore accounts, adding that if tax were paid on the income that this wealth generates, an extra $190bn would be available to governments every year.
The charity said as much as 30% of all African financial wealth was thought to be held offshore. The estimated loss of $14bn in tax revenues would be enough to pay for healthcare for mothers and children that could save 4 million children’s lives a year and employ enough teachers to get every African child into school.
Oxfam said it intended to challenge the executives of multi-national corporations in Davos on their tax policies. It said nine out of 10 WEF corporate partners had a presence in at least one tax haven and it was estimated that tax dodging by multinational corporations costs developing countries at least $100bn every year. Corporate investment in tax havens almost quadrupled between 2000 and 2014.
The Equality Trust, which campaigns against inequality in the UK, said Britain’s 100 richest families had increased their wealth by at least £57bn since 2010, a period in which average incomes declined.
Duncan Exley, the trust’s director, said: “Inequality, both globally but also in the UK, is now at staggering levels. We know that such a vast gap between the richest and the rest of us is bad for our economy and society. We now need our politicians to wake up and address this dangerous concentration of wealth and power in the hands of so few.”
Larry Elliott is the Guardian's economics editor and has been with the paper since 1988
