The Cities Refugees Saved

Mahira Patkovich was eight years old in 1997 when her family left Bosnia. After a long and complicated war, Muslim families like hers had found themselves without jobs, food, and any semblance of safety. So they sought refuge in America.
The first year in their new home in Utica, New York, Patkovich felt uprooted—torn from her childhood and everything she knew, and thrust into an alien environment. She knew no one and didn’t speak English. But as time went by, she began to acclimate.
“The next thing you know, you’re home,”she says in a recent mini-documentary by New American Economy, a bipartisan immigration reform group, and Off Ramp Films. “This is home.”
Patkovich, the film shows, is now thriving. She works at the office of the Oneida County Executive, owns a small business, and is on her way to a master’s degree. She is also pregnant, and excited to raise her first-born in a community she loves.
Utica—it’s clear—saved Patkovich and her family. But the truth is: They’re helping to save this town as well. Like many Rust Belt cities, Utica suffered enormously in the second part of the 20th century, losing jobs and bleeding out residents as major employers like General Electric and Lockheed Martin shuttered or left the Mohawk Valley.
Adam Bedient, director of photography and editor at Off Ramp Films grew up in the nearby town of Clinton in the 1980s and ’90s. He wasn’t tracking Utica’s trajectory too closely then, in part, because not much was happening there. What he remembers of Utica in that era is a typical fading factory town, a place where shuttered storefronts and exposed bricks belied neglect. “Foundationally, there were beautiful things there, they just didn’t look cared for,” he says.
Now, he’s working on a full-length feature about the refugee communities in Utica, and when he drives through town, he finds it simmering with new life. Old buildings are getting refurbished. Construction cranes bob up and down. And at the center of town is a long-vacant historic Methodist church that has been renovated and converted into a beautiful mosque—a symbol of the new Utica.
“It’s really symbolic—it was previously a church that was going to be torn down,” Bedient told CityLab. “The Bosnian community bought it from the city, and now it’s a part of the skyline.”
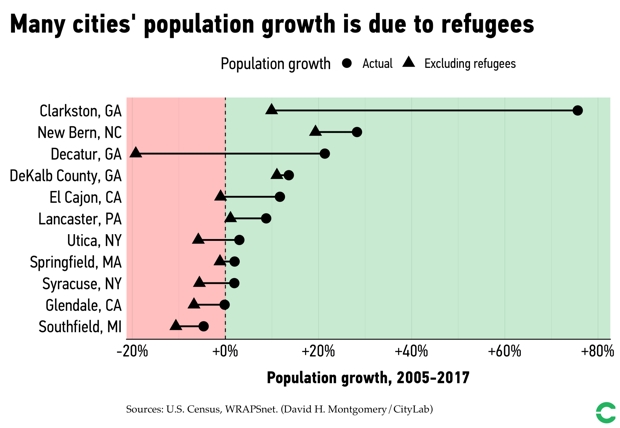
For CityLab, NAE crunched the numbers on the 11 cities that have resettled the most refugees per capita between 2005 and 2017 to gauge how welcoming these newcomers affected overall population. In almost all cases, refugee resettlement either stemmed population loss or reversed it completely. Without its new Bosnian community, for example, Utica would have faced a 6 percent population drop. With them, the city saw a 3 percent gain.
But what Andrew Lim, NAE’s director of quantitative research, found surprising was that this list didn’t just include industrial towns hungry for newcomers—places like Syracuse, New York, and Springfield, Massachusetts; it also features places in the South and Sunbelt. Take Clarkston, Georgia, for example, a diverse Atlanta exurb of 13,000 (whose young mayor you may recognize from a recent episode of Queer Eye). Since the 1970s, Clarkston has taken in tens of thousands of refugees from various parts of Asia, the Middle East, Africa, and Europe. In Bitter Southerner, Carly Berlin recently explained how it gained its nickname as the “Ellis Island of the South.”
As many white residents fled farther out to more fashionable developing Atlanta suburbs, Clarkston became perfect for refugees, with its hundreds of vacated apartments and access to public transportation, a post office, and a grocery store, all within walking distance. The little city became one of now 190 designated resettlement communities across the country.
Using the data NAE extracted from the Census Bureau and from the Department of Homeland Services, CityLab’s David Montgomery created this nifty chart to show exactly how much refugees boosted or stabilized population in these 11 cities:
But the pipeline that funneled refugees into cities like Utica is being closed up. In 2018, the Trump administration lowered the maximum number of refugees it takes in for the third year in a row—to 30,000, which is the lowest in three decades. Resettlement agencies, from Western Kansas to Florida, are having to close shop.
Some places are already seeing the effects. In cities with large concentrations of refugees and refugee services, recent arrivals have been waiting for loved ones to join them. Because of the slash in numbers being accepted, some of these people have been thrust into uncertainty. Muslim refugees from countries listed in the final travel ban have been doubly hit, and may not be able to reunite with their families at all.
But the effects of the Trump-era refugee policy don’t just affect individual families. In Buffalo, New York—another Rust Belt city that has been reinvigorated by new residents from refugee communities—medical clinics have closed down, housing developments have stalled, and employers have been left looking for employees, The Buffalo News reported. The loss for refugees hoping to come to America appears to also be a loss for the communities they might have called home
The biggest argument for refugee resettlement is that it is a moral imperative, many advocates argue. Refugees are human beings fleeing terrible circumstances; assisting them is just the right thing to do. Foes of taking refugees—most notoriously, White House advisor Stephen Miller, who is quoted as saying that he would “be happy if not a single refugee foot ever touched American soil again” in a new book by a former White House communication aide—point to the perceived costs and dangers of taking in more. Past analyses shows little basis to that fear. In fact, cities with large refugee populations have seen drops in crime, per a previous NAE’s analysis. And according to NBC News, an intelligence assessment that included inputs from the FBI concluded that refugees did not pose a major national security threat. The Trump administration dismissed its findings.
Of course, it does cost federal, state, and local money to equip refugees with the tools they need to start a new life. But once they are settled, refugees open up businesses, hire locals, buy homes, and pay taxes. Muslim refugees like Patkovich have had outsized economic and demographic impacts on cities like Detroit, Michigan and Nashville, Tennessee. In fact, the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) drafted a report in 2017, later obtained by the New York Times, showing that refugees brought in far more revenue from taxes, business permits, and other fees than they consumed in public benefits: “Overall, this report estimated that the net fiscal impact of refugees was positive over the 10-year period, at $63 billion.” The Trump administration rejected this report as well.
This kind of wrangling over the true impact of refugees doesn’t get much traction in Utica, where refugees now make up almost a quarter of the city’s population, Bedient says. It’s not really up for debate at this point—“it’s a part of the city's identity now,” he says.
[Tanvi Misra is a staff writer for CityLab covering immigrant communities, housing, economic inequality, and culture. She also authors Navigator, a weekly newsletter for urban explorers (subscribe here). Her work also appears in The Atlantic, NPR, and BBC]
