Carrier Workers Are Livid After Facing Layoffs Despite Trump’s Promises
In These Times
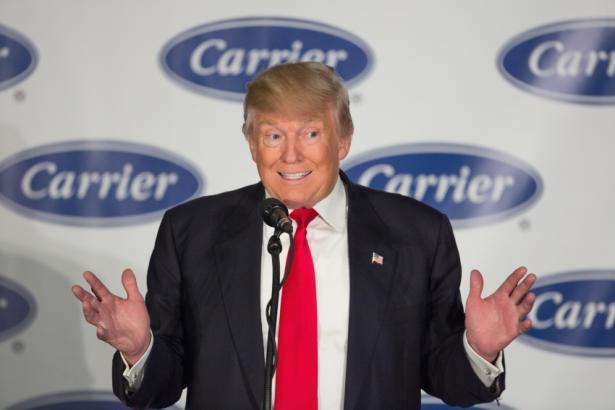

The fine print of Trump’s deal has now turned into reality for Carrier’s Indianapolis employees. Roughly 340 workers lost their jobs in July. The last round of layoffs mean 250 workers will clock in in for their final shifts today despite Trump’s pledges.









Spread the word