Until recently, it was hard to know just how good the superrich are at avoiding taxes. Public statistics are oddly quiet about their contributions to government coffers, a topic of legitimate interest in democratic societies.
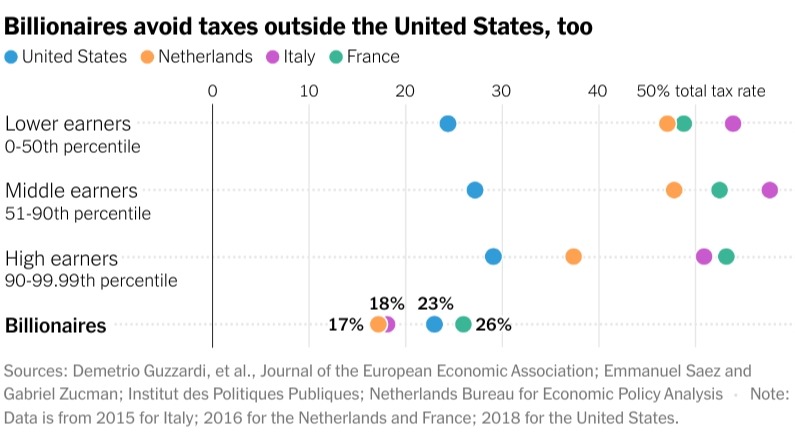
Over the past few years, I and other scholars have published studies and books attempting to fix that problem. While we still have data for only a handful of countries, we’ve found that the ultrawealthy consistently avoid paying their fair share in taxes. In the Netherlands, for instance, the average taxpayer in 2016 gave 45 percent of earnings to the government, while billionaires paid just 17 percent.
Why do the world’s most fortunate people pay among the least in taxes, relative to the amount of money they make?
The simple answer is that while most of us live off our salaries, tycoons like Jeff Bezos live off their wealth. In 2019, when Mr. Bezos was still Amazon’s chief executive, he took home an annual salary of just $81,840. But he owns roughly 10 percent of the company, which made a profit of $30 billion in 2023.
If Amazon gave its profits back to shareholders as dividends, which are subject to income tax, Mr. Bezos would face a hefty tax bill. But Amazon does not pay dividends to its shareholders. Neither does Berkshire Hathaway or Tesla. Instead, the companies keep their profits and reinvest them, making their shareholders even wealthier.
Unless Mr. Bezos, Warren Buffett or Elon Musk sell their stock, their taxable income is relatively minuscule. But they can still make eye-popping purchases by borrowing against their assets. Mr. Musk, for example, used his shares in Tesla as collateral to rustle up around $13 billion in tax-free loans to put toward his acquisition of Twitter.
Outside the United States, avoiding taxation can be even easier.
Take Bernard Arnault, the wealthiest person in the world. Mr. Arnault’s shares in LVMH, the luxury goods conglomerate, officially belong to holding companies that he controls. In 2023, Mr. Arnault’s holdings received about $3 billion in dividends from LVMH. France — like other European countries — barely taxes these dividends, because on paper they are received by companies. Yet Mr. Arnault can spend the money almost as if it were deposited directly into his bank account, so long as he works through other incorporated entities — on philanthropy, for instance, or to keep his megayacht afloat or to buy more companies.
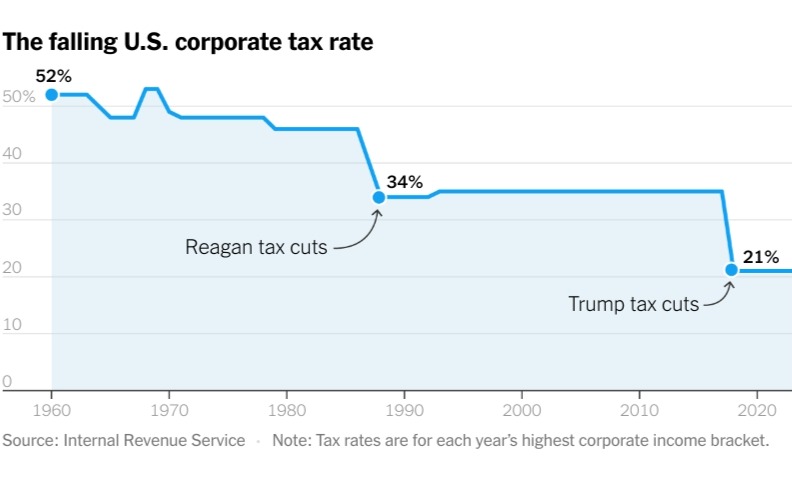
Historically, the rich had to pay hefty taxes on corporate profits, the main source of their income. And the wealth they passed on to their heirs was subject to the estate tax. But both taxes have been gutted in recent decades. In 2018, the United States cut its maximum corporate tax rate to 21 percent from 35 percent. And the estate tax has almost disappeared in America. Relative to the wealth of U.S. households, it generates only a quarter of the tax revenues it raised in the 1970s.
So what should be done?
One obstacle to taxing the very rich is the risk they may move to low-tax countries. In Europe, some billionaires who built their fortune in France, Sweden or Germany have established residency in Switzerland, where they pay a fraction of what they would owe in their home country. Although few of the ultrawealthy actually move their homes, the possibility that they might has been a boogeyman for would-be tax reformers.
There is a way to make tax dodging less attractive: a global minimum tax. In 2021, more than 130 countries agreed to apply a minimum tax rate of 15 percent on the profits of large multinational companies. So no matter where a company parks its profits, it still has to pay at least a baseline amount of tax under the agreement.
In February, I was invited to a meeting of Group of 20 finance ministers to present a proposal for another coordinated minimum tax — this one not on corporations, but on billionaires. The idea is simple. Let’s agree that billionaires should pay income taxes equivalent to a small portion — say, 2 percent — of their wealth each year. Someone like Bernard Arnault, who is worth about $210 billion, would have to pay an additional tax equal to roughly $4.2 billion if he pays no income tax. In total, the proposal would allow countries to collect an estimated $250 billion in additional tax revenue per year, which is even more than what the global minimum tax on corporations is expected to add.
Critics might say that this is a wealth tax, the constitutionality of which is debated in the United States. In reality, the proposal stays firmly in the realm of income taxation. Billionaires who already pay the baseline amount of income tax would have no extra tax to pay. The goal is that only those who dial down their income to dodge the income tax would be affected.
Critics also claim that a minimum tax would be too hard to apply because wealth is difficult to value. This fear is overblown. According to my research, about 60 percent of U.S. billionaires’ wealth is in stocks of publicly traded companies. The rest is mostly ownership stakes in private businesses, which can be assigned a monetary value by looking at how the market values similar firms.
One challenge to making a minimum tax work is ensuring broad participation. In the multinational minimum tax agreement, participating countries are allowed to overtax companies from nations that haven’t signed on. This incentivizes every country to join the agreement. The same mechanism should be used for billionaires. For example, if Switzerland refuses to tax the superrich who live there, other countries could tax them on its behalf.
We are already seeing some movement on the issue. Countries such as Brazil, which is chairing the Group of 20 summit this year and has shown extraordinary leadership on the issue, and France, Germany, South Africa and Spain have recently expressed support for a minimum tax on billionaires. In the United States, President Biden has proposed a billionaire tax that shares the same objectives.
To be clear, this proposal wouldn’t increase taxes for doctors, lawyers, small-business owners or the rest of the world’s upper middle class. I’m talking about asking a very small number of stratospherically wealthy individuals — about 3,000 people — to give a relatively tiny bit of their profits back to the governments that fund their employees’ educations and health care and allow their businesses to operate and thrive.
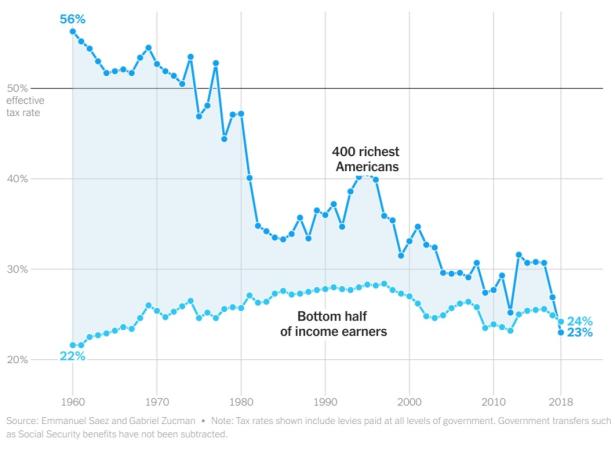
The idea that billionaires should pay a minimum amount of income tax is not a radical idea. What is radical is continuing to allow the wealthiest people in the world to pay a smaller percentage in income tax than nearly everybody else. In liberal democracies, a wave of political sentiment is building, focused on rooting out the inequality that corrodes societies. A coordinated minimum tax on the superrich will not fix capitalism. But it is a necessary first step.

Spread the word